A lot says Dr SK Gupta a senior consultant in the cardiology department of the Indraprastha Apollo Hospitals!
He explains the differences and just how to tackle the situations. Read on!
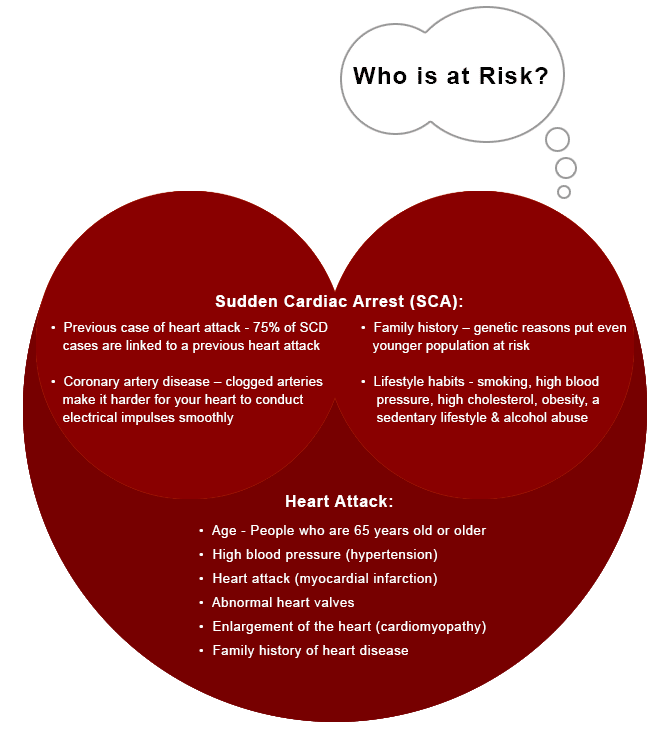
A heart attack occurs when a blocked artery prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching a section of the heart. If the blocked artery is not reopened quickly, the part of the heart normally nourished by that artery begins to die.
This heart disease is a result of plaque buildup in the arteries, which blocks blood flow and heightens the risk for heart attack.
The longer a person goes without treatment, the greater the damage.
Sudden Cardiac Arrest (SCA) is a life-threatening condition when the heart abruptly stops functioning without any warning. It is the sudden unexpected loss of heart function leading to breathing difficulty and loss of consciousness.
Death occurs due to the malfunctioning of the heart’s electrical system and may affect a person with or without prior diagnosed cardiac diseases.
The unexpected death, occurring usually within 60 minutes from onset of the symptoms, stops the blood flow to the brain and other vital organs.
A heart attack is a "circulation" problem and sudden cardiac arrest is an "electrical" problem.
How are these two heart conditions connected?
Heart attack and sudden cardiac arrest are linked.
SCA can occur during a heart attack or post a heart attack.
An episode of heart attack increases your chances of getting a sudden cardiac arrest.
Symptoms
Sudden cardiac arrest symptoms are immediate and drastic which include sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing and loss of consciousness.
Sudden cardiac arrest often occurs with no warning; death occurs within three minutes if no treatment is given.
Heart attack symptoms aren't always obvious; but they can be severe.
One may experience a number of symptoms, including:
- Discomfort in the left side of chest/upper abdomen
- Dyspnea (Shortness of breath from any type of exertion)
- Cold sweat
- Vomiting/nausea
- Confusion
Note: Unlike a cardiac arrest, during a heart attack the heart does not stop beating.
Treatment and Prevention:
A heart attack patient should be rushed to the hospital within an hour and required treatment should be delivered.
A case of cardiac arrest is however more grave and fatal.
Cardiac arrest is reversible if treatment is given within minutes. It is important for the patients who are at risk of cardiac arrest to undergo diagnostic tests and opt for treatment suggested by the cardiologist.
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator (ICD):
An implantable cardioverter defibrillator (ICD) is a small device implanted under your skin. It continuously automatically monitors your heartbeat, detects an increase in heart rate and delivers precisely calibrated electrical shocks to restore a normal heart rhythm and saves life.








 © 2025
© 2025