Photographs: Reuters Nupur Pavan Bang
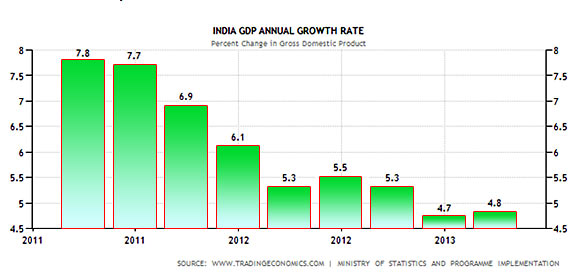
Slowdown in the economy
The issue of the relationship between development of financial systems (including currency markets) and economic fundamentals has been a much studied topic.
The numerous studies on the topic confirm a positive and significant relationship between them. Successful financial sector reforms should translate into higher GDP for a country.
Dr Manmohan Singh, the architect of India's liberalisation policies and the person credited with ending license raj, had slipped into oblivion in the last few years.
He has been often criticised of being a puppet at the hands of Sonia Gandhi, increasingly so in the past couple of years when the Indian economy experienced a slowdown and loss of investors' confidence.
Lack of reforms has pushed the GDP down to 4.8 per cent in the last quarter.
Click on NEXT for more...
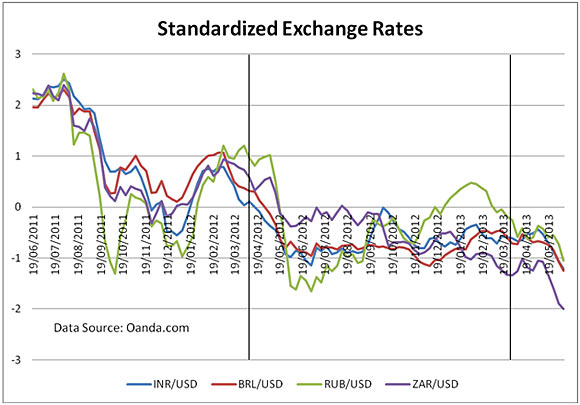
The Falling Rupee
Last two years
In the last two years, Indian rupee has depreciated by 25 per cent, Brazilian real by 33 per cent, Russian rouble by 15 per cent and South African rand by 47 per cent.
We are not considering the Chinese yuan as its value is not market determined.
The global economic crisis caused a slowdown and period of uncertainty amongst most of the BRICS nations, as also the developed and the other emerging nations.
In the financial year 2011-2012, the events in the Euro region were widely blamed for the depreciating currencies against the US dollar. The domestic woes of high trade and fiscal deficits, high inflation, low confidence, lack of will for reforms, were also adding to the fall of the rupee.
Click on NEXT for more...
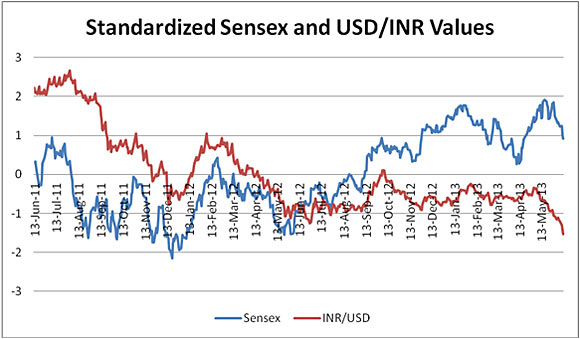
The Falling Rupee
Half-hearted reforms
Concerns about the falling rupee and constant threat of downgrade by the rating agencies, forced the government to make some noise regarding reforms.
Inflation was also tamed to some extent by keeping interest rates high, following which RBI cut interest rates.
These measures cheered the markets and stabilized the exchange rate for about three quarters between June 2012 and April 2013, as something was better than nothing.
But now, with poor corporate earnings, continued bad news in terms of the economic numbers, and flight of foreign financial investments to safer assets, both the rupee and the markets have been sliding.
Click on NEXT for more...
The Falling Rupee
Image: People walk past a roadside currency exchange vendor in the old quarters of Delhi.Photographs: Adnan Abidi/Reuters
The impact
While talking to a seasoned investor from Kolkata, he told me, "I have a bad feeling about this. My son is happy as he works in the US and for him a depreciating rupee means more money in his Indian bank account.'
But what about the value of our currency? If our currency is not valued, if there is no demand for it, how will the economy and the stock market grow? Who would want to invest in an economy whose currency is not valued? I would feel much more confident if our currency was strong."
The conversation explains the impact that the falling rupee has.
While non-residential Indians who send back money home may be happy about it, people who study abroad or who want to travel abroad for medical or tourism purposes, will not be happy about it.
Similarly, firms who are net importers, their costs will go up many folds, while firms who are net exporters, may be able to capture more market by giving discounts or offering better prices.
Click on NEXT for more...
The Falling Rupee
Photographs: Sanjay Sawant/Rediff
Revival
If we look at the data for the last week alone, most of the currencies have depreciated heavily against the dollar owing to the better than expected US jobs data and the improved outlook for the US economy.
While it is easy to blame the global economic cues once again (like many other times in the past), the fact of the matter is that if our economy was sound and the investor confidence intact, it would have been easier to revive the rupee.
It may not be so easy now due to the lack of these.
Nupur Pavan Bang is senior researcher, Centre for Investment, Indian School of Business, Hyderabad. She can be reached at: Nupur_bang@isb.edu




article