| « Back to article | Print this article |
PICS: ISRO successfully launches indigenous cryogenic engine
In a New Year gift to the nation, the Indian Space Research Organisation on Sunday successfully launched a Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle with an indigenous cryogenic engine from the spaceport of Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Sriharikota, entering a select club of nations.
With this launch, ISRO became the sixth space agency in the world after the United States, Russia, Japan, China and France to have tasted success with an indigenous cryogenic engine.
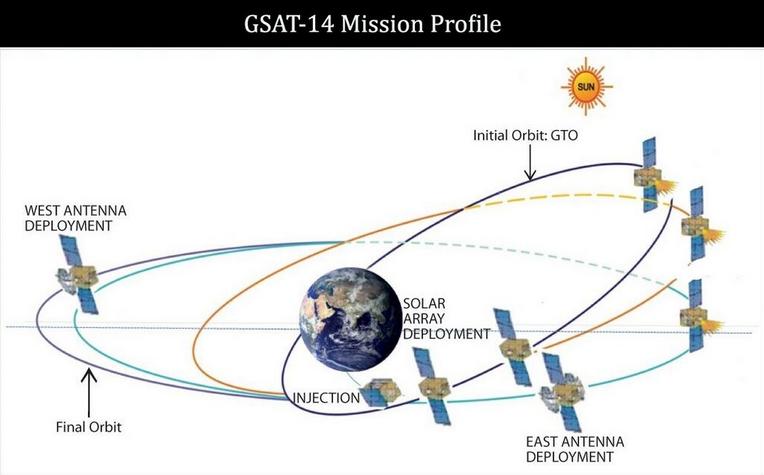
"I am extremely happy and proud to say team ISRO has done it. The Indian cryogenic engine and stage performed as predicted, as expected for this mission and injected precisely the GSAT-14 communication satellite into intended orbit," a jubilant K Radhakrishnan, ISRO chairman said from the Mission Control Room soon after the launch vehicle placed the 1,982 kg GSAT 14 satellite into the intended orbit.
Click NEXT to read further...
PICS: ISRO successfully launches indigenous cryogenic engine
Launching a GSLV with an indigenous cryogenic engine has been a major challenge for ISRO since 2001 after multiple unsuccessful attempts. Only four of earlier seven attempts have succeeded.
The GSLV D5's scheduled launch on August 19 last year was called off in the eleventh hour after a fuel leak, following which the ISRO moved the vehicle back to the VehicleAssemblyBuilding and rectified the defect.
Sunday’s launch is India's eighth flight of GSLV and also the fourth developmental flight of GSLV. During this flight, the indigenously developed Cryogenic Upper Stage was flight tested for the second time.
The GSAT-14 is India's 23rd geostationary communication satellite, as four of GSAT-14’s predecessors were launched by GSLV during 2001, 2003, 2004 and 2007, respectively.
Click NEXT to read further...
PICS: ISRO successfully launches indigenous cryogenic engine
The GSAT-14 would join the group of India's nine operational geostationary satellites. The primary objective of this mission is to augment the in-orbit capacity of extended C and Ku-band transponders and provide a platform for new experiments.
The GSAT-14 will be positioned at 74 degree East longitude and co-located with INSAT-3C, INSAT-4CR and KALPANA-1 satellites.
PICS: ISRO successfully launches indigenous cryogenic engine
Click on MORE to see another PHOTO features...