| « Back to article | Print this article |
PHOTOS: Views from the International Space Station
The bright sun, a portion of the International Space Station and Earth's horizon are featured in this image photographed during the STS-134 mission's fourth spacewalk in May 2011.
The image was taken using a fish-eye lens attached to an electronic still camera.
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
Thin Blue Line
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
Katia from space
The picture, taken with a 12-mm focal length, was captured at 14:09:01 GMT. Later in the day Katia was upgraded to hurricane status.
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
This is what the moon looks like from space
Said Garan, "We had simultaneous sunsets and moonsets." For Garan and the rest of the station crew, this extraordinary event is a daily occurrence. Since the station orbits the Earth every 90 minutes, each day the crew experiences this about 16 times a day.
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
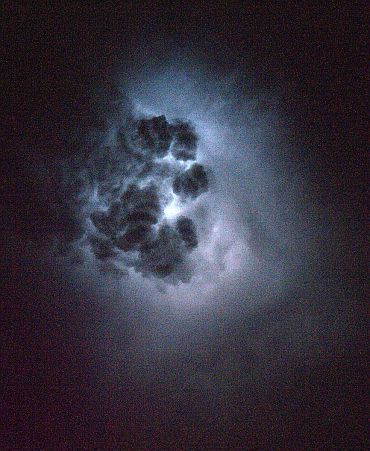
Lightning over Brazil
Nespoli, a member of the Expedition 27 crew, first visited the station in 2007 as a member of the STS-120 crew aboard space shuttle Discovery to deliver the Italian-built Harmony node.
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
Nile river delta at night
One of the fascinating aspects of viewing Earth at night is how well the lights show the distribution of people. In this view of Egypt, the population is shown to be almost completely concentrated along the Nile Valley, just a small percentage of the country's land area.
The Nile River and its delta look like a brilliant, long-stemmed flower in this photograph of the southeastern Mediterranean Sea, as seen from the International Space Station. The Cairo metropolitan area forms a particularly bright base of the flower. The smaller cities and towns within the Nile Delta tend to be hard to see amidst the dense agricultural vegetation during the day. However, these settled areas and the connecting roads between them become clearly visible at night. Likewise, urbanized regions and infrastructure along the Nile River becomes apparent.
Scattered blue-grey clouds cover the Mediterranean Sea and the Sinai, while much of northeastern Africa is cloud-free. The thin yellow-brown band tracing the Earth's curvature at the top of the image is airglow, a faint band of light emission that results from the interaction of atmospheric atoms and molecules with solar radiation at an altitude of approximately 60 miles (100 kilometers).
This astronaut photograph was taken by the Expedition 25 crew on October 28, 2010, with a Nikon D3S digital camera using a 16 mm lens.
Click on NEXT to see more PHOTOS...
Celestial mountains
The Tien Shan mountain range is one of the largest continuous mountain ranges in the world, extending approximately 1,550 miles (2,500 kilometers) roughly east-west across Central Asia. This image taken by the Expedition 27 crew aboard the International Space Station provides a view of the central Tien Shan, about 40 miles (64 kilometers) east of where the borders of China, Kyrgyzstan, and Kazakhstan meet.
The uplift of the Tien Shan, which means celestial mountains in Chinese, like the Himalayas to the south, results from the ongoing collision between the Eurasian and Indian tectonic plates. The rugged topography of the range is the result of subsequent erosion by water, wind and, in the highest parts of the range, active glaciers.
Two high peaks of the central Tien Shan are identifiable in the image. Xuelian Feng has a summit of 21,414 feet (6,527 meters) above sea level. To the east, the aptly-named Peak 6231 has a summit 6,231 meters, or 20,443 feet, above sea level.
Click on MORE to see another interesting PHOTO feature...