Significant progress has been made in protecting hundreds of thousands Rohingya refugees in Bangladesh since they fled violence in Myanmar, but lives “will once again be at risk” if funding is not urgently secured, United Nations officials have said on the eve of the first anniversary of a military crackdown that forced them to flee their country.
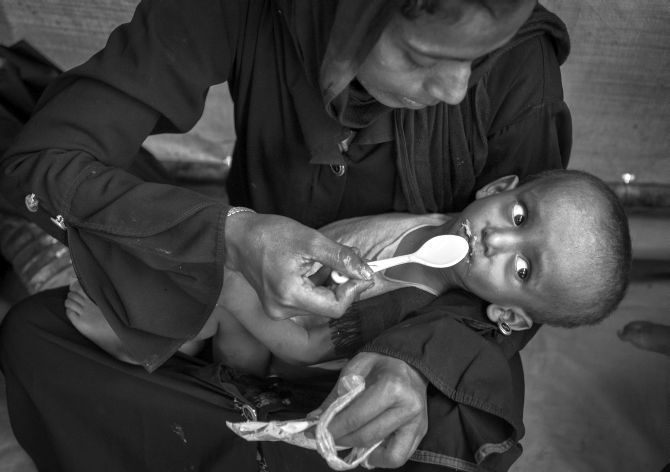

Nearly 700,000 Rohingya, most of them Muslims, have been displaced from Rakhine since the military began a crackdown on militants last August. Most have crossed the border into Bangladesh, joining the 200,000 refugees already there.
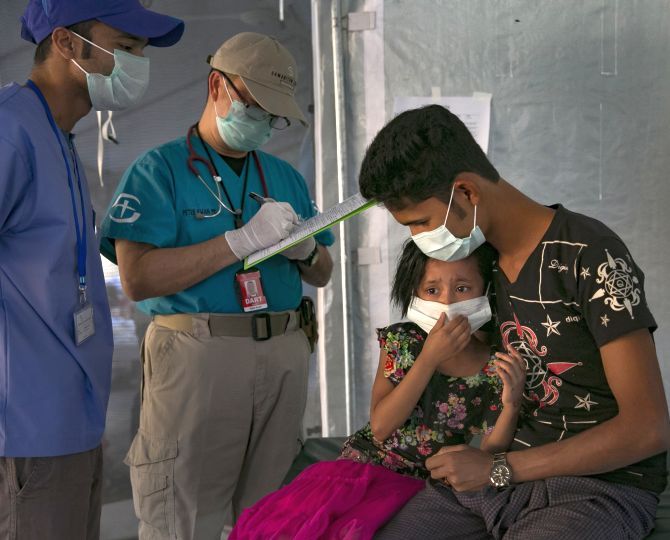
Deputy Director-General of Emergency Preparedness and Response for the UN World Health Organisation Peter Salama told journalists in Geneva that deadly disease outbreaks had been held at bay in Bangladesh’s Cox’s Bazar despite “all the conditions being in place for a massive epidemic”.
Outbreaks of measles, diphtheria, polio, cholera and rubella have been contained, he said, noting that “thousands of lives” had been saved so far, thanks to the joint efforts of the Bangladesh government, WHO and partners.
“We need to sustain the vigilance for early warnings of infectious diseases,” Salama said. “That is still a major risk due to the environmental situation, the poor sanitation, the massive overcrowding, the way these people are being housed and we need to maintain our ability to scale-up outbreak response as required.”
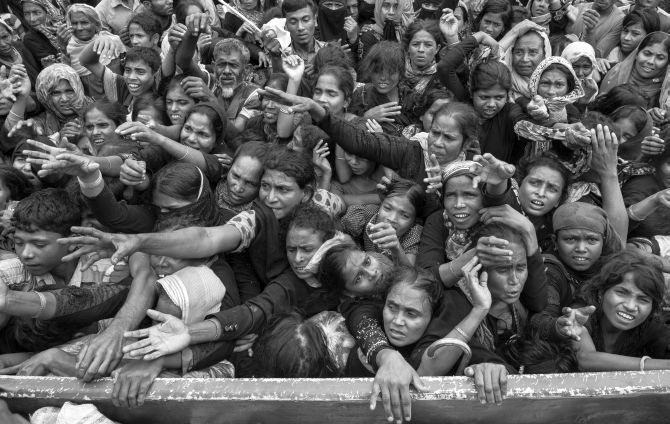

His call to scale up help was echoed in Geneva by IOM, the UN migration agency, spokesperson Joel Millman.
“This was the fastest growing refugee crisis in the world and the challenges have been immense,” he said, highlighting comments by the agency’s Chief of Mission in Bangladesh Giorgi Gigauri. “Countless lives have been saved thanks to the generosity of the Government of Bangladesh, the local community and donor s and the hard work of all those involved in the humanitarian response. But we now face the very real threat that if more funding is not urgently secured, lives will once again be at risk.”
One year on from the exodus sparked by a military operation likened to ethnic cleansing by UN human rights chief Zeid Ra’ad al Hussein, more than 720,000 Rohingya people have arrived in Cox’s Bazar in southern Bangladesh.
They have joined an estimated 200,000 Rohingya refugees who were previously displaced.
One of the camps, Kutupalong, shelters more than 600,000 refugees, making it the largest and most densely populated refugee settlement in the world, according to the Office of the UN High Commissioner for Refugees.
In addition to the challenge of providing people’s basic needs -- shelter, water and sanitation and healthcare -- the agency has carried out huge engineering work to reduce the risk of landslides and flooding. This also involved mobilising and training hundreds of refugee volunteers to serve as first responders in the event of a natural disaster, although the camps have largely withstood the adverse weather.
Another key area of concern is the health of some 60,000 pregnant Rohingya women in the camps. Many of them suffered gender-based violence “either prior or during the course of their flight” from Myanmar, WHO’s Salama said, adding that only one fifth of them will give birth in a suitable healthcare facility.

Partner agency UNHCR also underlined the calls for the international community to step up support for the Rohingya, who are stateless and unable to return to Myanmar. This is despite the UN’s signing of an official Memorandum of Understanding with the Government of Myanmar in June, to help establish conditions conducive for the safe, dignified and sustainable repatriation of the Rohingya.
According to OCHA, the UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs, the mainly Muslim Rohingya communities that have stayed in Rakhine state require urgent -- and in some cases lifesaving -- help.
Some 660,000 people are in need across Rakhine state including more than 176,000 in Northern Rakhine, OCHA spokesperson Jens Laerke said.
“We stand ready to go there as soon as access allows,” he added.
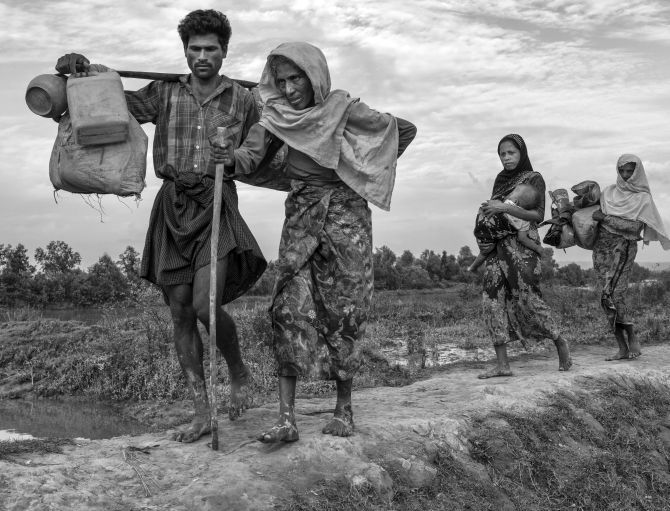

“Most humanitarian organisations that have been working in Northern Rakhine state for years have still not been able to resume programmes and services for these population which are some of the most vulnerable in the world.”
To date, the $950 million (Rs 6,628 crore) Rohingya 2018 appeal is only just over 30 per cent funded.











 © 2025
© 2025