Photographs: Amit Dave/Files/Reuters Business Standard
The worst victims of increasing water stress are the cities, many of which are already facing an acute water crisis.
A recent study by the Hyderabad-based National Geophysical Research Institute has predicted that several large cities and their satellite towns will run out of locally available water, including groundwater, in the next few years.
Hyderabad may be the first to go dry, followed by Delhi and Chennai, among others.
An earlier World Bank-sponsored study ranked Chennai and Delhi as the most vulnerable cities in Asia in terms of daily water availability.
Please . . .
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15
Water scarcity: Hyderabad, Delhi will be worst hit
Image: This file photograph shows women tsunami survivors carrying pots of drinking water in tsunami-hit Nagapattinam, Tamil Nadu.Photographs: Babu/Reuters
The unrealistic pricing of water and its imprudent and wasteful use in the absence of regulatory mechanisms are the chief reasons for this crisis.
Several previous finance commissions have recommended that water rates recover not only operational and management costs, but also part of the investment in water projects.
Even so, most states have not revised prices for decades; some others have done so reluctantly and inadequately.
The National Water Policy, 2002, said water rates should make the users realise its scarcity value.
Please . . .
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15
Water scarcity: Hyderabad, Delhi will be worst hit
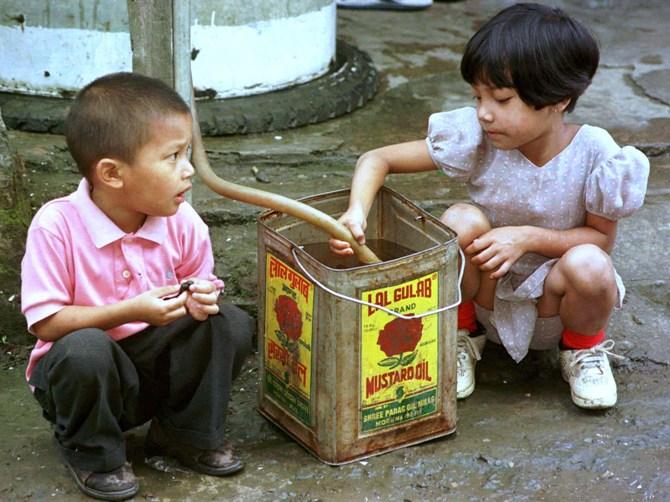
Image: Children fill a cannister with drinking water from a public tap in Aizawl, Manipur..Photographs: Reuters
The unrealistic pricing of water and its imprudent and wasteful use in the absence of regulatory mechanisms are the chief reasons for this crisis.
Several previous finance commissions have recommended that water rates recover not only operational and management costs, but also part of the investment in water projects.
Even so, most states have not revised prices for decades; some others have done so reluctantly and inadequately.
The National Water Policy, 2002, said water rates should make the users realise its scarcity value.
Please . . .
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15
Water scarcity: Hyderabad, Delhi will be worst hit
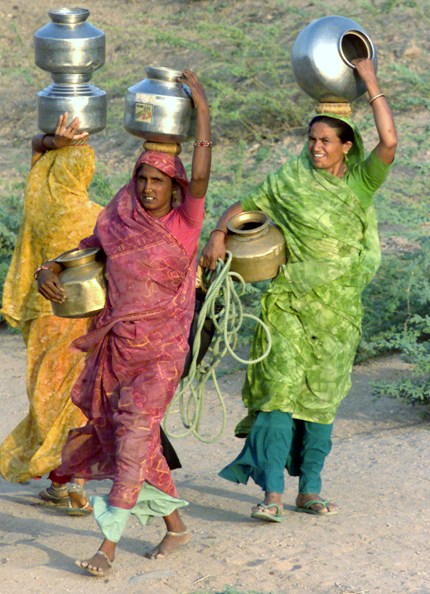
Image: Villagers carry vessels containing drinking water in the village of Kundaliya in the drought affected Gujarat.Photographs: Kamal Kishore/Reuters
This pointed phraseology was replaced in the 2012 version of the policy with the recommendation that water be treated as an ‘economic good’.
That policy did call for curtailing subsidies on power for running water pumps -- again, not fully implemented.
Regrettably, the bulk of the rainwater that India receives every year -- especially in the monsoon season, which accounts for 75-80 per cent of total precipitation -- is allowed to run off wastefully to the seas.
Hydrology experts maintain that at least 16 per cent of it should be guided to subsurface water reserves.
Please . . .
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15
Water scarcity: Hyderabad, Delhi will be worst hit
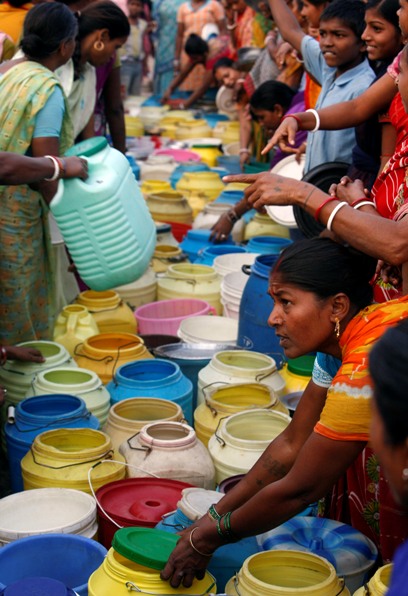
Image: Residents of a slum stand with empty water containers as they wait to collect drinking water from a tanker at a roadside in Kolkata.Photographs: Parth Sanyal/Reuters
However, at present, less than half of that amount is so preserved.
Some cities have ordered large building complexes to install rainwater harvesting systems.
Compliance is dismal.
Worse, civic authorities are themselves not serious about rainwater conservation.
Much of the water falling on public lands is allowed to run off, choking the drains and leading to waterlogged roads.
Please . . .
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15
Water scarcity: Hyderabad, Delhi will be worst hit
Image: Torsha, a four-year-old orphan elephant drinks water in Jaldapara Wildlife Sanctuary.Photographs: Rupak De Chowdhuri/Reuters
The solution to the impending water emergency, therefore, lies in conserving water in underground aquifers, as well as in surface storage structures, such as ponds, lakes and reservoirs.
Many countries have created adequate storage capacity through dams to cater to their needs over two or more years.
In India, on the other hand, the total water stocking capacity in its 85 main reservoirs is only about 253 billion cubic metres, hardly sufficient to meet a year’s requirement. Unless conservation and storage are enhanced and water is priced adequately to deter its reckless use, it may be difficult to make the country water-secure.
Please click here for the Complete Coverage of Budget 2014 -15







article