 | « Back to article | Print this article |
Smart tips to crack law entrance exams
Law aspirants must focus on mastering English, follow developments in the legal field and improve awareness of current affairs.
Today, there are several entrances for admission to law degrees at colleges across the country.
These include CLAT, LSAT, SET, IPU-CET and NLU Delhi (AILET), to name a few.
Typically, there are five subjects or test-areas which a candidate needs to prepare well to crack CLAT and all other law entrance exams except LSAT-India, which has a completely different pattern.
We explore these areas below.
Mastering English
The language of law, English assumes the most important role in a law entrance exam. A student ideally needs to master three areas of English:
- Vocabulary
- Grammar and Sentence Correction
- Reading Comprehension
a. Building vocabulary
Expanding your vocabulary on a daily basis from every possible source is important -- from your daily newspaper to your textbooks, or from books like Word Power Made Easy by Norman Lewis.
Similarly, doing some grammar and sentence correction exercise daily is important from any good book on objective English like English is Easy of Chetananand Singh or a book on similar subject by RS Agarwal.
The popular school grammar text-book High School English Grammar and Composition by Wren and Martin can be another good book for mastering basics of grammar.
To master comprehension, a wide reading habit as well as practice from past papers is needed.
A two-month plan and working two hours daily on English can do the magic even for students from non-English medium.
b. Common types of questions
Based on past papers analysis, the types of English Questions for CLAT can be summarised as follows:
- English Comprehension
- Fill up the blanks
- Spelling test
- Vocabulary -- synonyms, antonyms including Latin, French and legal terms
- Phrasal verbs, idioms and phrases
- Para jumbles
- Sentence correction tests
The author Anand Prakash Mishra holds an LLB and LLM from the Faculty of Law, University of Delhi and works at Jindal Global Law School. He has been a founding member and academic head of Universal Institute of Legal Studies, New Delhi. He can be reached at anandpmishra@gmail.com.
Please click NEXT to continue reading...
Brush up your GK, knowledge of world affairs
General Knowledge/ Current Affairs
GK usually has the highest weightage in a law entrance exam. GK questions – both static and current - constitute no less than 25 per cent of the paper in any such exam.
Reading a good newspaper daily and taking notes are the best way to build GK.
Reading a good competition magazine could be your safest bet (at least six past issues, better a year).
However, if a student has not done GK throughout the year, The Hindu Diary of Events of the preceding year can be a great help. During preparation, students are advised to take note of all important sports events thoroughly.
Important topics
Aspirants should focus on international economic, trade and finance related issues and also similar developments relating to UN and its agencies, WTO, World Bank & IMF etc.
Candidates should go for a good GK book like Pearson's coupled with a latest yearbook by Penguin or Malayala Manorama or India of Publications Division, Government of India.
Students can also read GK content of the last six months at a good GK portal.
Logical Reasoning
The purpose of the logical reasoning section is to test the student's ability to identify patterns, logical links and rectify illogical arguments.
It will include a wide variety of logical reasoning questions such as syllogisms, logical sequences, analogies, etc.
However, visual and non-verbal reasoning are usually not tested in law entrance exams.
Managing time is key
Students may rely upon a good textbook on analytical reasoning like the one by MK Pandey or RS Agarwal.
Thorough practising on selected areas based upon past paper analysis from any one of the mentioned books would suffice.
Time management is very important and it is always prudent to move on to the next question without wasting too much time on one particular question.
What is important to master this area is regular practise of at least a couple of reasoning exercises for at least two months.
Legal Aptitude/Legal Awareness
This area focuses either legal reasoning or legal GK questions.
To master legal reasoning questions, candidates must learn and understand legal principles relating to laws of torts, contracts, crimes, family law and general principles of law.
Candidates may opt for a good guidebook like Universal's Guide to LLB or SS Guide (especially for DU).
Also the Civics/Political Science school text books can be great help in mastering Constitution and Indian Polity, a major area for legal knowledge questions.
Legal aptitude, math skills equally important for law
Legal Aptitude/Legal Awareness
This area focuses either legal reasoning or legal GK questions.
To master legal reasoning questions, candidates must learn and understand legal principles relating to laws of torts, contracts, crimes, family law and general principles of law.
Candidates may opt for a good guidebook like Universal's Guide to LLB or SS Guide (especially for DU).
Also the Civics/Political Science school text books can be great help in mastering Constitution and Indian Polity, a major area for legal knowledge questions.
Keeping track of legal news
Information about courts, lawyers and judges is important in Legal GK. One needs to keep track of legal news and developments in the country.
Whether it is a legislative development in Parliament or a landmark judgement from the Supreme Court or High Courts, it would be important for the exam.
For mastering legal awareness or Legal GK questions, again reading a good newspaper like The Hindu and taking note or every important legal development in the country on a regular basis is extremely important.
Mathematics
In this section the candidates will be tested only on "elementary" mathematics ie, Math that is taught till Class 10.
The areas one needs to be comfortable with are percentages, profit and loss, ratio, proportion and variation, simple equation, averages, time and work, time and distance, ie, arithmetic and nothing else.
Just master the concepts and formulae and practising from an Objective Mathematics book like that of RS Agarwal would suffice.
You may check your school text-books of classes 8 to 10 also to recapitulate past learning.
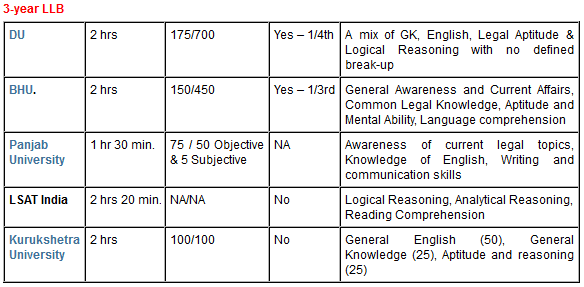
Generally 3-year LL.B exams like that of DU do not ask questions from Mathematics.
Major exams and paper patterns
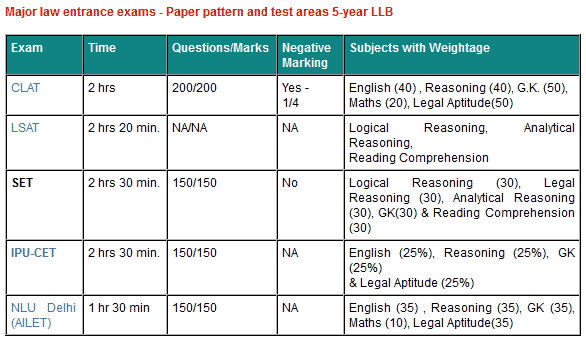
LLB entrance test of Delhi University
The focus in Delhi University LLB entrance remains on three areas namely GK, English & Legal Aptitude.
Sometimes logical and analytical reasoning questions are also asked in good numbers but not always.
Students should have a balanced strategy for all the four subjects i.e. GK, English, Legal Aptitude & Logical Reasoning.
If we analyse past years papers of DU, GK emerges as the most important area. Even 100 or more questions out of a total of 175 questions were from GK/Current Affairs in the past few years.
Also in DU, most of the Legal Aptitude questions are from Legal GK or Legal Awareness and very few questions from Legal Reasoning.
LSAT-India Examination
Law School Admission Test or LSAT-India exam is conducted by PearsonVue in India on behalf of Law School Admission Council, USA.
Jindal Global Law School and IIT Kharagpur (Rajiv Gandhi School of Intellectual Property Law) are the two most important law schools accepting LSAT scores.
Students can visit the test website to find a full-length sample question paper and sample questions in each of the test-areas, that is, Analytical Reasoning, Critical Reasoning and Reading Comprehension.
Students can buy the Official LSAT India Handbook at the time of making applications or they can buy from the market the popular Kaplan LSAT Book for a thorough preparation.
There is no General Knowledge, Grammar, Legal Reasoning and Mathematics, in this examination.
Negative marking for CLAT 2013
In a recent development, a significant change was announced for CLAT 2013. Scheduled to be held on May 13, in this edition of CLAT, 0.25 marks will be deducted for every incorrect answer.
The paper comprises 200 multiple-choice questions of one mark each across the following sections - English including comprehension, GK/Current Affairs, Elementary Mathematics, Legal Aptitude and Logical Reasoning.
Quick tips to ace the exam


