 Sugarcane, which is grown by no more than 1.1 million farmers, consumes 70 per cent of water available in Maharashtra for irrigation. In contrast, about 10 million jowar, pulses and oilseeds farmers get only 10 per cent of irrigation water, points out Abhishek Waghmare.
Sugarcane, which is grown by no more than 1.1 million farmers, consumes 70 per cent of water available in Maharashtra for irrigation. In contrast, about 10 million jowar, pulses and oilseeds farmers get only 10 per cent of irrigation water, points out Abhishek Waghmare.

A resident of Pune, Maharashtra’s second-most developed city, uses five times as much water as her counterpart in Latur, the district most ravaged by drought in the south-central Marathwada region.
That’s the extent of water inequality in Maharashtra, India’s most developed state, according to an IndiaSpend analysis of statewide water use, characterised by disproportionate availability and consumption of water across regions, crops and consumers.
The coastal region of Konkan - occupying a tenth of the state’s landmass and home to 14 per cent of its population (except Mumbai) - contains more than half of Maharashtra’s water, according to government data.
The populous, dry and rain-shadow regions of western, central Maharashtra, Marathwada and Vidarbha, retain the other half, clashing with each other and neighbouring states for water.
But the natural imbalance of water does not make drought inevitable. That happens because water has been deliberately routed to areas where it is already plentiful and to farmers who are politically powerful.
Sugarcane - which is grown on 4 per cent of the state’s farms - consumes 70 per cent of water available for irrigation, IndiaSpend reported earlier, although no more than 1.1 million farmers grow the lucrative cash crop. In contrast, about 10 million jowar (sorghum), pulses and oilseeds farmers get no more than 10 per cent of irrigation water.
“The earlier Congress–Nationalist Congress Party-led government was entrenched in sugar politics with 13 of the 30 Cabinet ministers owning or controlling sugar factories,” Parineeta Dandekar, associate coordinator of South Asian Network for Dams, Rivers and People, wrote in her analysis of the sugarcane situation in Maharashtra.
Water inequality is a natural phenomenon
There are five river basins in Maharashtra: Krishna, Godavari, Tapi, Narmada and a combined basin of westward flowing rivers in the coastal Konkan region.
Of these, three are agriculturally important - Krishna, Godavari and Tapi. They cover 89 per cent of the state’s area; 0.4 per cent of the state falls under the Narmada river basin.
The Konkan basin drains 10.9 per cent of the land, while containing 55 per cent of the state’s water.
The Krishna basin drains most parts of Western Maharashtra, the prosperous districts of Kolhapur, Pune, Satara, Sangli and Solapur, and some perennially drought-plagued areas, such as eastern swathes of Sangli, Satara and Solapur districts.
The Godavari basin covers the drought-hit regions of Marathwada and Vidarbha.
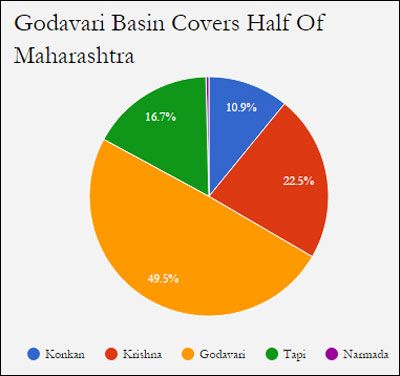
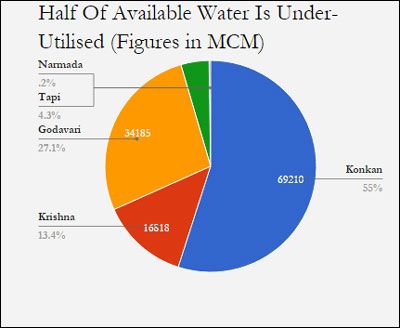

Source: White Paper on Irrigation, Government of Maharashtra
MCM: Million Cubic Metres
Of the 125 billion cubic metres (BCM) surface water available in Maharashtra’s river basins, most of the 69 BCM in the Konkan region goes unutilised, according to this 2012 Maharashtra government White Paper on Irrigation.
In contrast, the 17 BCM in the Krishna and 34 BCM in the Godavari basins are insufficient for the regions they water.
“In Maharashtra, sugarcane cultivation, which is on (sic) less than 4 per cent of the total cropped area of the state, takes away almost 70 per cent of irrigation water in the state, leading to massive inequity in the use of water within the state,” said the sugarcane price policy report, 2014-15, issued by the Commission on Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP).
The CACP tabulates the share of irrigation water used by major crops in Maharashtra.
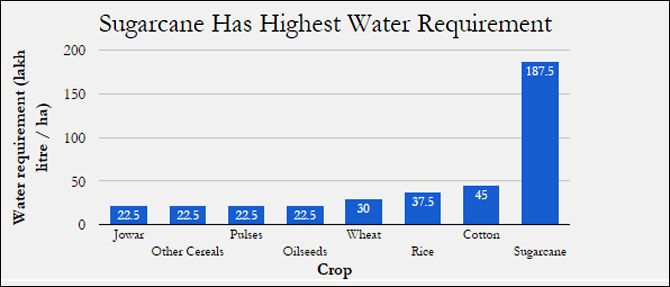
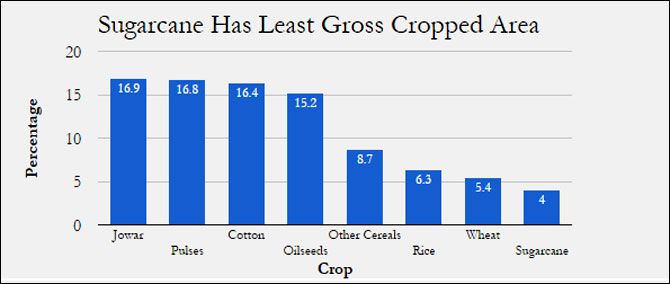
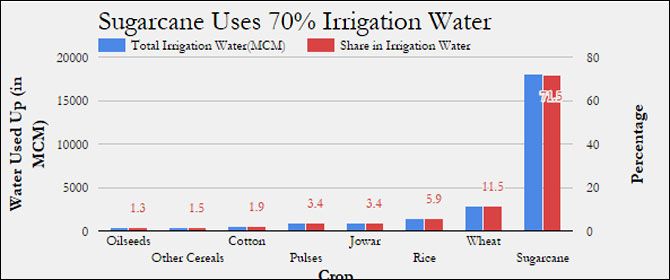
Source: Sugarcane Price Policy 2014-15, Commission on Agricultural Costs and Prices
How sugarcane corners irrigation water
Sugarcane is the only crop in Maharashtra which is wholly irrigated. Irrigation water is available for no more than 9 per cent of pulses and 4 per cent of oilseeds.
About 10 million farmers grow jowar, pulses and oilseeds - no more than a tenth of these farms are irrigated, as we said - and these crops use about 2.2 million litres of water per hectare, about 2,000 MCM of water through the year.
Sugarcane’s 1.1 million farmers use 18.7 million litres per hectare and consume 18,000 MCM - nine times that of jowar, oilseeds and pulses - annually across the state.
More developed the city, more the water used
Urban water consumption patterns are heavily tilted towards developed cities.
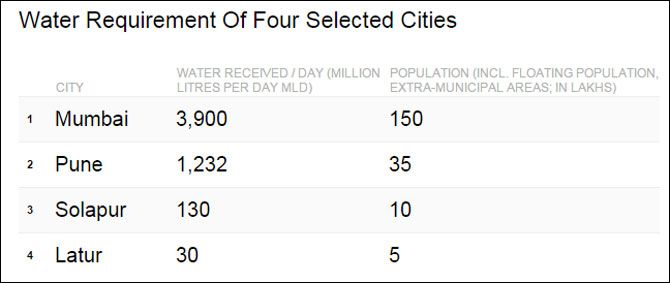
The city of Latur in Marathwada consumes 60 litres per person daily, while an average Mumbaikar uses around 260 litres a day. The average daily use of water per person in Pune is 352 litres, according to IndiaSpend calculations, based on daily water requirements of these cities and the latest available population figures.

The–officially set–rural-urban water imbalance
A village with less than 20,000 people should get 40 litres of water per person per day, five litres less than the water prescribed to flush a toilet in a city such as Mumbai - these are the standards set in 1993 by the Bureau of Indian Standards in its Code of Basic Requirements.
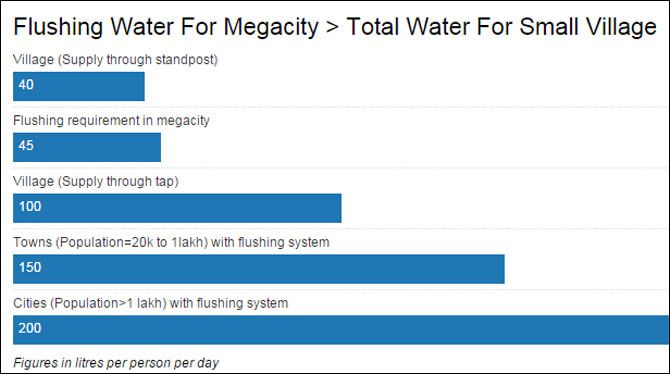
The standards also recommend reduced water supply to poorer localities in urban areas.
In 2015, the Kelkar Committee on balanced regional development in Maharashtra recommended 140 litres per capita per day across rural and urban Maharashtra.
The recommendation has not yet been included in the state’s water policy.
Abhishek Waghmare is an analyst with IndiaSpend.
Photographs: Reinhard Krause/Reuters and Rupak De Choudhuri/Reuters
Powered by  Indiaspend.org is a data-driven, public-interest journalism non-profit
Indiaspend.org is a data-driven, public-interest journalism non-profit











 © 2025
© 2025